NeurOS System Architecture
NeurOS is architected as an open platform to accelerate research and development of cognitive systems. It provides, supports and enables:
- extensive built-in tools and component module libraries
- easy integration with external systems and technologies
- multiple development tools
- application portability without redesign to multiple operating system and system configuration platforms
- performance scalability via pipelined and partitioned dataflow parallelism across uni-processors, multi-processors, distributed and heterogeneous systems, without application redesign
- sharing and reuse of custom modules, sub-assemblies, applications and learned memory patterns
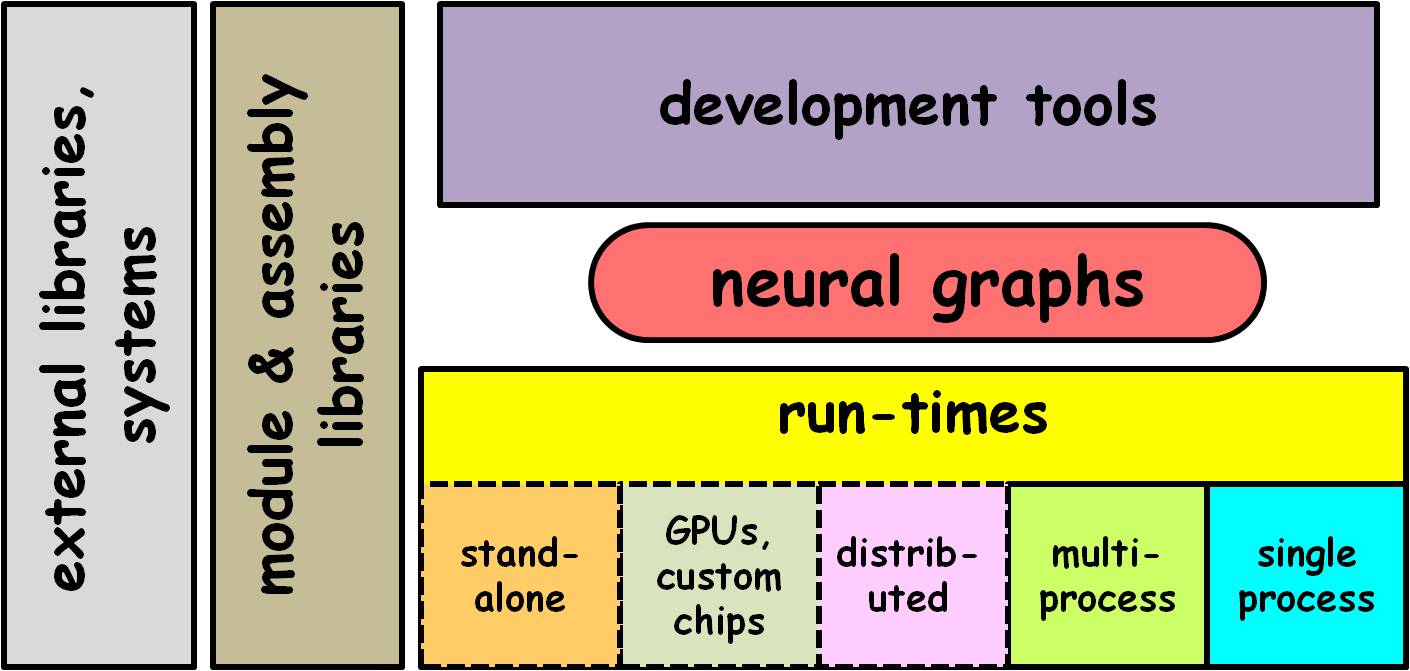
At the core are neural graphs. These are platform-independent representations of sub-graphs and whole applications. An XML file format allows easy interchange among tools and run-time systems, without requiring application redesign. Additional formats allow saving and reuse/sharing of learned memory pattern spaces.
Development tools edit neural graphs and provide debugging and visualization. The primary built-in tool is the NeurOS Designer IDE (Integrated Development Environment). It supports graphical editing of neural graphs via dragging and dropping of NeuroBlock modules from a extendable and customizable parts bin, pop-up parameter setting, custom wrapping and module development, memory pattern visualization, tracing, variable-speed execution and single-stepping, graphical activity monitoring, development scaffolding, hierarchical design, and other development and visualization aids.
NeurOS run-time systems enable neural graph execution on a variety of platforms. Courtesy of data flow rules, a neural graph can execute on a growing range of operating system and hardware configurations, as supported by NeurOS system development. Run-time support for stand-alone programs and custom GPU and neuromorphic hardware are planned.
Extensive built-in module libraries provide a wide range of general-purpose capabilities for inputs/senses, outputs/effectors, processing and memory. Modules have both design-time and platform-independent and dependent run-time components.
The initial NeurOS implementation, used to build and run all the example usages and applications, is written in Python using the Spyder IDE on Windows 7/8, with limited multi-processing capabilities. However, applications written in this version will port seamlessly to future design-time and run-time implementations on multiple platforms.
A more detailed presentation was given to the Boston Software Architecture, Development and Integration Meetup on 2017-09-14.